Apple's Novak Goes from Shop To Corporate Leader
Sean Novak went from being a young chemical engineer at Anoplate to manager of the surface finishing team at Apple Inc.
He found that partner in Sean Novak, a young chemical engineer who was hired by Anoplate out of Syracuse University to help meet customers’ rigid finishing specifications in the aerospace, defense, electronics, medical and optics industries.
“He hiked with me for four or five years, and I never would have become a Forty-Sixer if it wasn’t for Sean pushing and pursuing me to do it,” says Stevenson, Anoplate’s vice president of technology, who completed his 46 peaks and hiked with Sean as he finished his goal.
When they would reach the summit, Stevenson says Novak and he would spend time resting and talking about life’s more important journeys.
“Sean would always talk about his dream job, which was to be an engineering manager, travelling internationally and have eight or nine people working for him,” he says. “It was just talk, but you could see he was someday going to reach that.”
Three years later, Novak has reached the apex of his career (so far) as manager of the surface finishing team at Apple Inc., a Cupertino, California-based conglomerate that designs, develops and sells consumer electronics, software and online services.
Novak, a member of Products Finishing’s inaugural look at the top 40 Under 40 in the finishing industry, leads a team of 11 engineers specializing in the anodizing and plating of enclosures, connectors and internal components for Apple products, including the iPhone, laptops and computers, iPads and, most recently, the Watch.
His group recently developed a series of novel processes for anodized finishes for Apple’s new colors and custom alloys, including the first cosmetic 7000-series aluminum housing for the Apple Watch that was met with rave reviews across the globe.
“Apple has a lot of surface finishing challenges because we deal a lot with metals,” Novak says. “The transition has been from injection molded plastics to anodized aluminum products pretty much across the board.”

Milt Stevenson, left, and Anoplate hired Novak out of Syracuse University.
From Job Shop to Apple
The groundwork for Novak’s admittance into one of the top electronics companies in the world began in college as an intern at Intel applying PVD copper on to silicon wafers, but was later refined when Anoplate offered him a position right out of college in 2006.
“We interviewed numerous engineers that year, but you could tell Sean really stood out from the rest,” Stevenson says. “He was a very good chemical engineer, but he was also a very good collaborator. He worked very well solving problems with people across many disciplines. That is something you are always looking for in someone.”
When Mike Barnstead left MacDermid Enthone in 2013 to join Apple as the electroplating expert in 2013, he recruited Novak after seeing him in action at Anoplate.
The transition from a working job shop like Anoplate to solving the finishing challenges at a multi-billion dollar global corporation like Apple wasn’t that much of a leap, as Novak says the team he worked with at Anoplate often faced similar issues.
“It all comes down to thinking flexibly and relentlessly focusing on the details and the requirements,” he says. “At Anoplate we dealt with a quick-turn, high quality requirement military, aerospace and medical applications that were challenging, and it was a great learning ground for what I am doing now.”
One of the big challenges Novak’s team faced was the redesign of Apple’s iPhone 6 from the 6000-series aluminum to the harder 7000-series alloy, which meant adding zinc and magnesium, materials that are more difficult to work with and anodize.
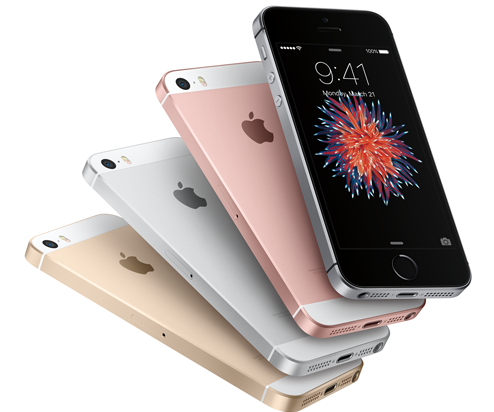

Apple says it created a new alloy that’s just as light as the 6000 series, but more durable. The company says it is 60 percent stronger than most aluminum, and one-third the density of stainless steel.
In addition to the new aluminum material, Novak and his team were tasked with the addition of four new lustrous colors of aluminum finish that Apple was introducing to its product lines: gold, silver, space gray and rose gold.
“It was a bit of a greenfield operation from the get-go at Apple,” he says. “We needed to come up with a disciplined process to how we would do process development. It could be a similar anodizing finish, but it could be a new product and a new color, and how do we go through and semi-standardize that process to take advantage of all the learnings in
the past.”
Apple says that, with the Watch, each case is machined and polished, then blasted with microscopic zirconia beads to get a consistent, satin texture. Novak’s team created a special anodizing process that creates a hard, clear outer layer to protect against scratches and corrosion.
“Sean’s team developed and implemented a series of procedures and techniques to enable high-volume anodized finishing to exacting standards, including color and durability requirements,” says Barnstead. “They also designed and implemented process control methodology for the high-volume production of a unique plating stack used on the iPad Pro models.”
Related Content
Filter Press Troubleshooting and Optimization
Zachary Beckman of Haviland Enterprises Inc. discusses proper filter press maintenance for optimization of wastewater treatment systems.
Read MoreNASF/AESF Foundation Research Project #122: Electrochemical Approaches to Treatment of PFAS in Plating Wastewater - 6th Quarterly Report
The NASF-AESF Foundation Research Board has selected a project on addressing the problem of PFAS and related chemicals in plating wastewater streams, studying PFAS destruction via electrooxidation and electrocoagulation. This sixth quarter report covers the continued assessment of eight perfluoroalkyl acids PFAAs most commonly found in wastewaters, by electro-oxidation with a Magnéli phase Ti4O7 anode across a range of anodic potentials in solutions, exploring the reaction mechanisms. To summarize, the PFAAs start to exhibit degradation behavior when the anodic potential reaches a level where water oxidation occurs, suggesting that the hydroxyl free radicals generated via water oxidation play a role in PFAA degradation.
Read MoreUltrafiltration Membranes, Filter Elements for Improved Industrial Water Reuse
Ultrafiltration membranes help with water reuse in a variety of applications.
Read MoreEPA Readying Fall Nationwide PFAS Survey of Metal Finishing Industry to Inform New Water Discharge Rule
NASF continues discussions with US EPA on the agency’s plans for a nationwide survey of the metal finishing industry on its use of PFAS. NASF plans to review the draft survey and provide feedback to the agency prior to its distribution. Surveys will likely go to a wide range of job shop and captive operations and are scheduled to be sent out in the fall.
Read MoreRead Next
Powder Coating 4.0: Smarter, Faster, More Efficient and Connected
New tools reduce cost and waste, lower manufacturing footprint of powder coating operations.
Read MoreEpisode 42: An Interview with Robin Deal, Hubbard-Hall
Hubbard-Hall wastewater treatment specialist Robin Deal discusses the latest trends in wastewater management.
Read MoreThe 2024 Ford Mustang: All the Colors Available
Although Chevrolet has announced the end of the Camaro and Dodge is offering “Last Call” editions of the Charger and Challenger, the Ford Mustang is launching to its seventh generation.
Read More