Electrocoating Q&A: Film Thickness Options
What type of epoxy ecoat do most automotive companies use for their steel parts?
#automotive
Q. What type of epoxy ecoat do most automotive companies use for their steel parts? What thickness do they use on their parts?
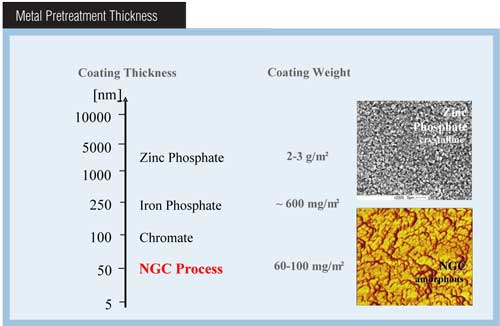
A. The corrosion performance of a coating system is heavily influenced by the pretreatment used over the steel substrate and under the ecoat. Automotive companies use zinc phosphate, zirconium or other specialized pretreatments prior to applying the ecoat.
Featured Content
The film thickness requirement for automotive steel parts varies greatly depending on the function of the parts (structural or not), and the type of environmental road conditions during vehicle use. Often, the vehicle location determines the type of exposure.
Because the film thickness requirement is specific to each particular part and function, the answer to your question will be generic about the different types of ecoats auto companies use.
The typical applications of epoxy ecoats in the automotive industry, as a single-layer final coating system or as a base primer for subsequent coating layers, is classified into three categories: low-film, medium-film and heavy-film applications.
Low-film ecoats are designed and operated to provide film-thickness ranges between 15 to 22 microns. The low-film applications provide good corrosion performance for interior applications, parts high under the hood or skin parts that will receive further coating treatments, such as doors and hoods. From an application standpoint, low-film ecoats are known to provide excellent self-limiting capabilities and high throw-power performance for processing high or dense coating loads, such as those encountered in automotive assembly plants.
Medium-film ecoats typically provide deposition film-thickness ranges between 25 to 35 microns. The medium-film thickness applications provide excellent corrosion performance for structural or steering components, and parts that are exposed to extreme environmental road corrosion conditions. These ecoats are mostly used by Tier-One and Tier-Two parts suppliers.
Heavy-film ecoats are designed and formulated to provide deposited films of 35 to 50 microns. These heavy-film ecoats provide excellent corrosion performance under extreme corrosive environments, and are sometimes used for parts and components that are exposed to extreme corrosive, gravel and chipping conditions. Typical parts coated with heavy-film ecoats are those structural and steering components exposed to the road. From an application standpoint, and inherent to the high thickness applications, heavy-film ecoats provide low throw-power capability and are not typically used to coat high or dense processing loads.
The film thickness and type of electrocoat for coating automotive steel parts mostly depends on the final function and use of the part on the vehicle.
Originally published in the March 2016 issue.
RELATED CONTENT
-
Salt Spray Vs. Cyclic Corrosion Tests
Joseph Subda, ecoat specialist for Axalta Coating Systems, explains the difference between these two corrosion resistance tests.
-
Five Principles of Lean Manufacturing from Toyota Production Systems
Fostering Sustainable business and People success through new ways of thinking
-
A Protective Decorative Electrolytic Coloring Process for Aluminum
The main task of this work was to study the influence of the different parameters on the electrolytic coloring process for aluminum.