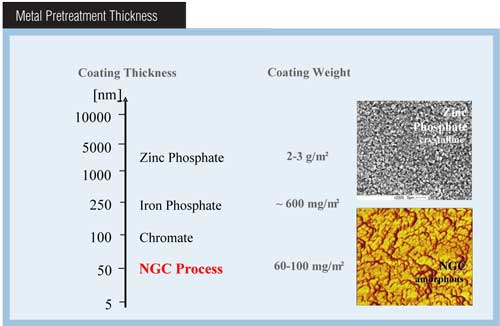
Repair of Rejected Parts
Question: I have seen from your web site that you can solve many painting problems and identify the correct way to do them.
Question:
I have seen from your web site that you can solve many painting problems and identify the correct way to do them. I was really impressed. At present, I work at a company that produces wall clocks, business instruments and other parts. Many of these products are painted using UV coatings on ABS plastic materials. We have problems with dust and scratches on surfaces after painting with the UV clear coating, and the products are rejected by our QC department. We would like to know how to repair the rejected products. We thank you for your help. C. T.
Answer:
Normally, rejected metal parts are spot repaired or stripped and repainted. Plastic parts are difficult to strip because of the sensitive nature of the substrate. A better approach would be to eliminate the cause of the rejects, in this case airborne dust and scratches.
Featured Content
Airborne dust can be eliminated by not allowing it into the spray booth and curing section of your paint line. Spray booth and cure oven (in your case the UV enclosure) make-up air must be filtered to remove airborne contamination. In addition, both these areas must be kept under positive pressure to prevent entrance of contaminated shop air. Of course, the parts must be dust-free before entering the spray booth.
Scratches can be eliminated by more careful handling of painted parts. This will require training of the operators, unloaders and shippers. Hopefully, since you are making high quality products, your factory workers are better trained than those at my former company. At my company the entry level position for a new worker was sweeper. The next level was painter.
RELATED CONTENT
-
Masking for Surface Finishing
Masking is employed in most any metal finishing operation where only a specifically defined area of the surface of a part must be exposed to a process. Conversely, masking may be employed on a surface where treatment is either not required or must be avoided. This article covers the many aspects of masking for metal finishing, including applications, methods and the various types of masking employed.
-
Curing Oven Basics
Simply heating up the substrate does not cure the coating. There are many variables to consider when choosing the best cure oven for your application...
-
Painting Over Powder Coating
How safely can they apply their wet paint over our powder coated parts?