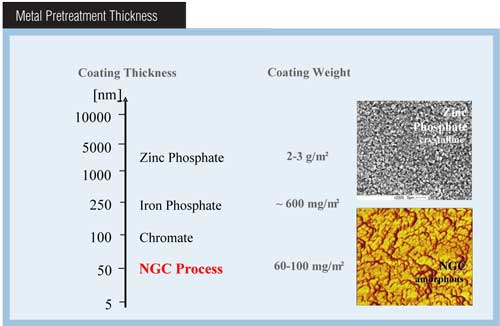
Rusting after Vibratory Finishing
Question: We are the leading company in our country in mass-finishing.
Question:
We are the leading company in our country in mass-finishing. We are doing a project for a customer who is manufacturing cylinders on which they want a prepainted finish. The present finishing process is shot blasting and then acid pickling.
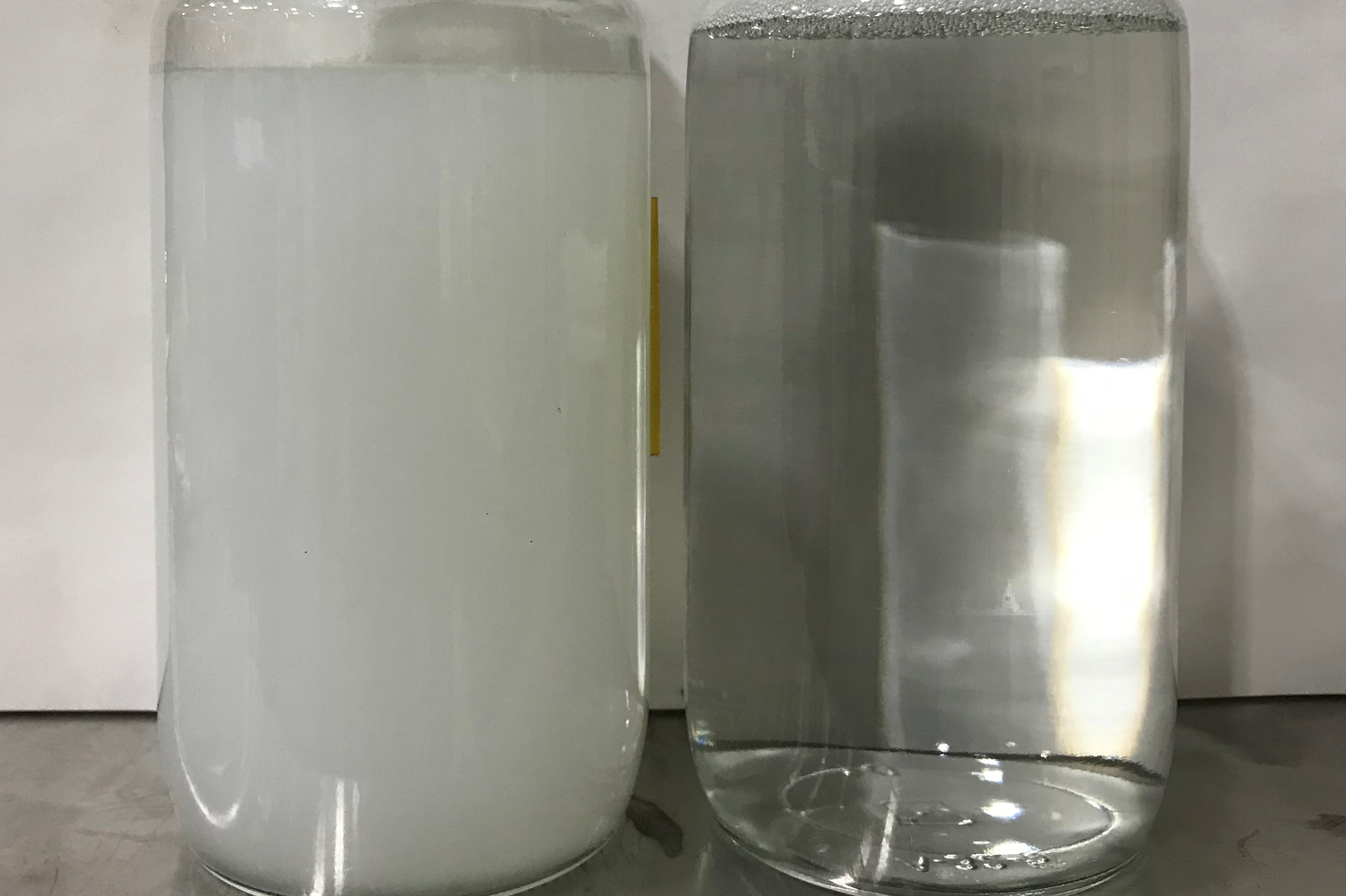
Now, we are trying to eliminate the process of shot blasting and acid pickling. Instead, we are using a trough vibratory finishing machine in which we are using aluminum oxide ceramic media with liquid chemical containing an acid (carboxylic) with a pH 3.5-4. During that process we achieved a very good surface for painting, but we are unable to prevent the product from rusting. In the meantime, to prevent rusting we have applied the water-based rust preventive chemical having pH 8.5-9.0. So, now we are protecting the product from rusting, but then the problem is we are not getting complete paint coverage ( on some of the components, paint adhesion is not achieved).
Featured Content
Can you suggest a way that we can put the chemical into the machine during the vibratory finishing process so we can dry it directly after finishing and the component will not rust? R. M.
Answer:
Perhaps there were some residual iron oxide particles that had not reacted with the oxalic acid present in the media liquid. They could have been transferred to the steel cylinder surfaces and manifested themselves as rust. These rust particles can be removed from the media liquid magnetically.
The water-based rust preventive may be acting like an interference coating (interfering with adhesion). If that is the case, it must be removed before painting. This is an additional step.
I am sure there is a rust inhibiting chemical available for addition to the media liquid to prevent rusting. Furthermore, you are not the only who has experienced this problem. I suggest you look in the Products Finishing 2003 Directory and Techology Guide, for help in this area.
RELATED CONTENT
-
Making the Best Choices in Mass Finishing
Choice of equipment, media and compounds has a major impact on your finishing applications.
-
What’s in a Burr?
An unclear definition has led to an industry standard for classifying burrs.
-
High Fives for the Surface Finishing Industry
National Surface Finishing Day offered what seems to have been a missing component in our makeshift gatherings over the past year, which is a chance to celebrate together.