Spraying Inside Tubes
Question: I hope my question is appropriate.
Question:
I hope my question is appropriate. I need to spray a liquid polymer mixed with ±15% reinforcing filler. The viscosity of this substance, after mixing, is ±10,000 cps. The surface to be sprayed is the inside of a cylinder, which is ±4.5 inches ID. The idea was to go the airless spraying route. We are already in possession of a high-pressure pump. The problem though is finding a nozzle with, preferably, a conical hollow spray pattern. Is it normal practice to do airless spraying with a high viscosity substance using hollow cone nozzles? Could you please assist with technical information on this matter? I accept the fact that quite a number of alternative methods exist, but the idea was to first investigate this one, since it appeared to be the most cost effective for us. Thank you very much. G.V.
Answer:
First, there are no inappropriate questions, only inappropriate answers. You have taken the correct approach. Airless spray is a natural for this type of application. Spraying inside tubes and cylinders is best done using a lance-mounted spray nozzle. The film thickness is controlled by the rate of travel in the tube. Lances come in several lengths to accommodate tube length. One suggestion I have is to replace the hollow cone nozzle with a 360-degree flat nozzle.
The other suggestion is, and this is important, stop spraying when the nozzle gets to the end of the tube during your trial runs. In the old days, when shirts cost $5 each, I ruined a new shirt three days in a row by not following that suggestion. (My wife is a saint.)
RELATED CONTENT
-
Understanding Paint Atomization
BASF coatings development expert Tim December explains how paint atomization works for both pneumatic spray applicators and high-speed rotary bell applicators.
-
Masking for Surface Finishing
Masking is employed in most any metal finishing operation where only a specifically defined area of the surface of a part must be exposed to a process. Conversely, masking may be employed on a surface where treatment is either not required or must be avoided. This article covers the many aspects of masking for metal finishing, including applications, methods and the various types of masking employed.
-
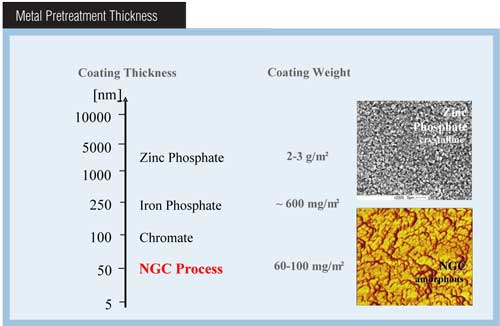
Phosphate Conversion Coatings
Types of phosphate conversion coatings, how to apply them, and their specific functions.