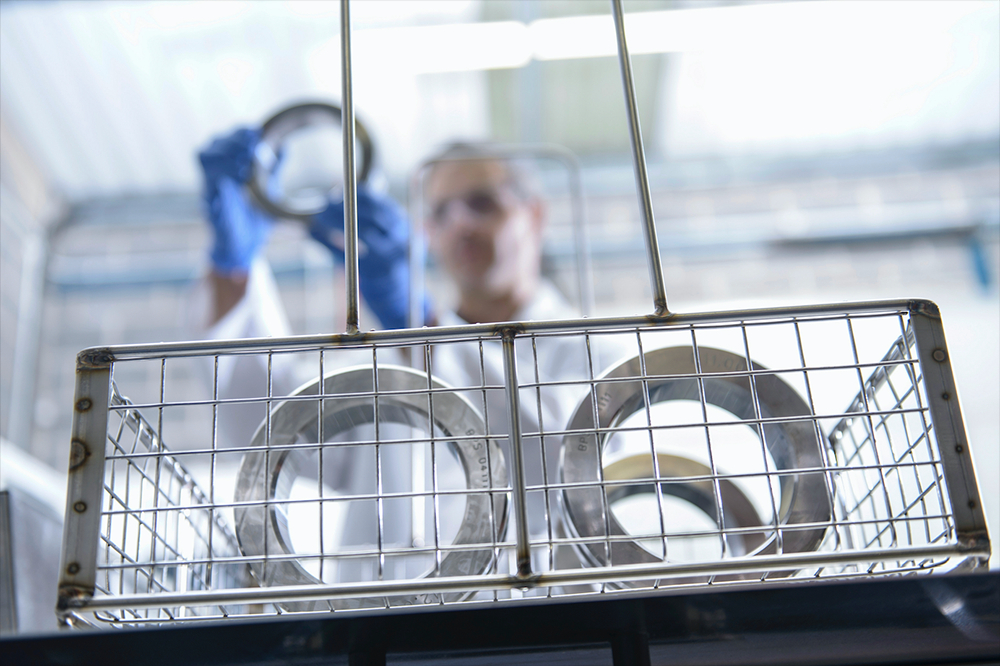
CERN Vacuum Group Finds New Method to Apply 'Getter' Coatings
The process allows accelerators such as electron synchrotrons to operate with better-focused beams and produce brighter radiation by bringing the steering magnets closer to the beams themselves.
#vacuum-vapor
From the article “Honey, I Shrunk the Vacuum Chambers!” by Achintya Rao on the CERN website:
It takes a lot of work to achieve nothingness. The beam pipes within particle accelerators are some of the emptiest regions in the universe. They are evacuated so as to prevent the accelerating particles from colliding with gas molecules in their path. The extreme vacuums inside these pipes are achieved by pumping out all the gasses within them and then coating their insides with layers of a special material called a “getter” to which stray molecules stick.
Featured Content
A team from the vacuum group at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, recently demonstrated a new method for applying getter coatings to much narrower beam pipes than ever before. This would allow accelerators such as electron synchrotrons to operate with better-focused beams and produce brighter radiation by bringing the steering magnets closer to the beams themselves.
The traditional method for applying the getter relies on producing a plasma of the coating material inside the pipes and using high voltage to deposit the material onto the inner walls. But the thinner and longer the pipe, the more difficult it is to produce a stable plasma; at a diameter of a few millimetres and a length of a few metres, it is impossible for the plasma to form, rendering this method unusable.
When faced with such challenges that push the limits of existing techniques, adopting inverse thinking helps. Rather than building the pipe first and applying the getter coating inside it, the engineers reversed the process. They first applied the getter coating to the outside of a temporary skeletal structure and then constructed the beam pipe around the coating by a metal-plating process. The skeletal structure, which is known as a “sacrificial mandrel” and is made of high-purity aluminium, was later dissolved, leaving behind a narrow vacuum chamber with a pre-applied getter coating.
“The key advantage of our technique is that it can also be used to make vacuum chambers with non-circular cross-sections,” says Lucia Lain Amador, the doctoral student who is leading the project. “And it is not limited to getter coatings – it can be used to apply other functional coatings in the future.”
Read more about the project HERE.
RELATED CONTENT
-
Mechanical Vapor Recompression Evaporation
MVRE is underutilized in the treatment of industrial wastewaters that are typical of metal fabricating and finishing industries. Increasing energy costs, rapidly decreasing freshwater resources, and growing sensitivity towards the environmental impact of industrial management practices are the driving forces in the development of more sustainable technology.
-
A Lustrous Example of Expanding a Plating Operation
Ohio’s Lustrous Metal Coatings Pins Growth on Acquiring Other Manufacturing Operations
-
Vacuum Deposition and Coating Options
This overview takes a look at vacuum deposition technologies as processes that may be used to create coatings that can be substituted for or enhances the properties of electroplated coatings. Initially, this work discusses trends in metal finishing and environmental regulation.