On-Site Treatment or Off-Site Disposal
Can you provide information on a pH/precipitation system that will speed up the process of removing metals and patina chemicals from wastewater?
#pollutioncontrol
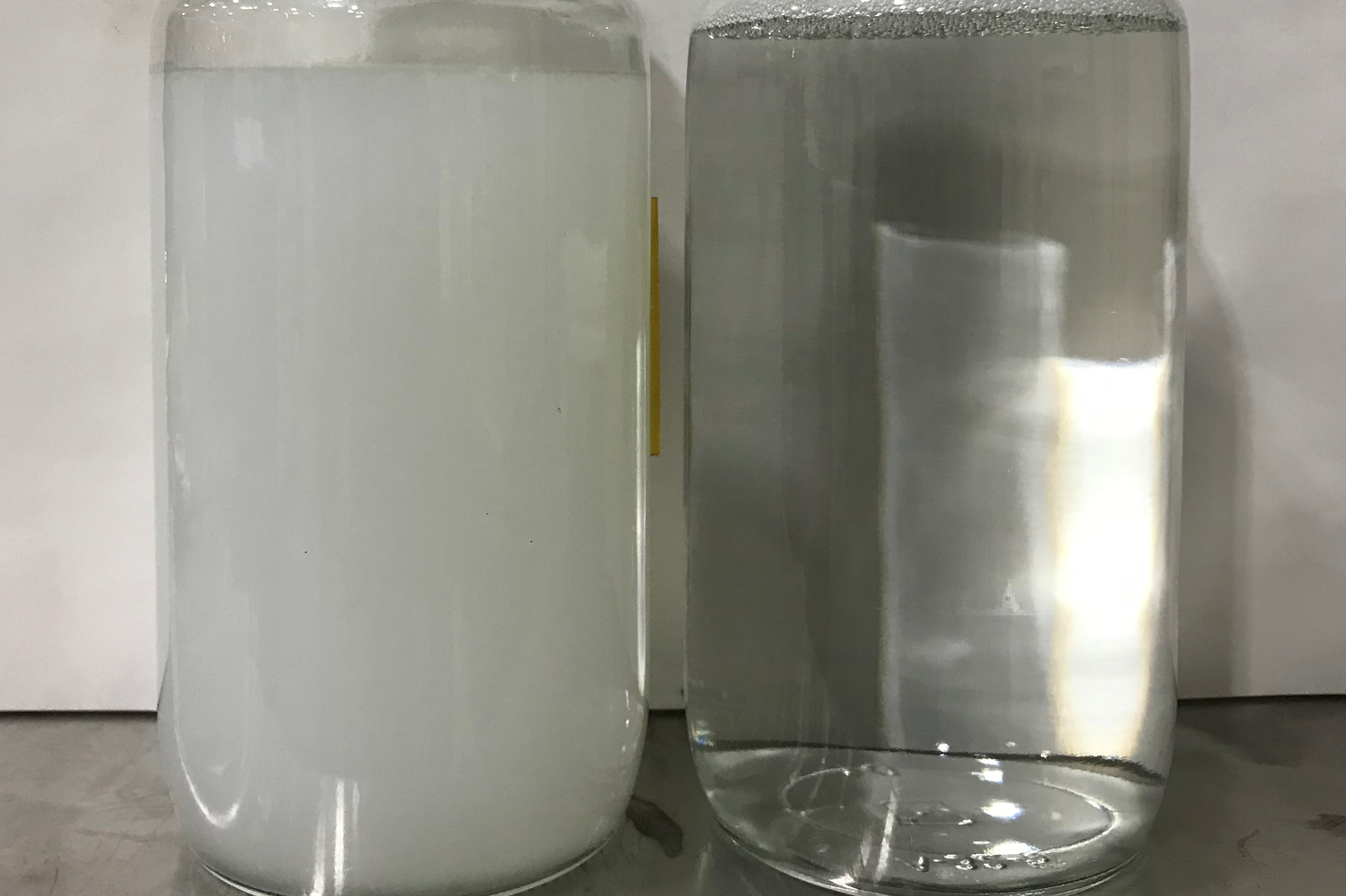
Q. We often apply oxidation patinas to metals then hand-rub them with water, using general purpose scouring pads to create highlight effects. The patinas are mostly cupric nitrate and others, and the metals are copper, zinc, pewter (tin), brass (copper and zinc) and bronze (copper and tin). We need to remove the metals and patina chemicals from the water sufficiently so that we can discharge it into the municipal sewer system. Currently, we capture the wastewater (1,000 gal per year maximum) and hold it for a year or more. I have heard of a pH/precipitation system that will speed up this process. Can you give me any information on this? D.B.
A. I am quite familiar with precipitation of the metals using pH adjustment followed by coagulant and/or polymer addition. There also are commercially available powders that can be added after pH adjustment; these powders contain coagulant, absorbent and polymer in one product.
Featured Content
You have two choices: batch treat wastewater on site, or store the wastewater and have it treated off site.
Due to your very small volume, I recommend batch treatment consisting of collection tank, conical bottom treatment tank with mixer, manual pH adjustment to about 9, chemical addition, clarification, and solids dewatering or filtration. When you add up the capital, operating, permitting, self-monitoring, recordkeeping and reporting costs for such a system and its discharge into your city’s sewer system, it likely will run you more than $5 per gal of wastewater generated.
An alternative to discharging to the sewer is to dispose of this wastewater off site at a cost of much less than $5 per gal. First, determine if this wastewater is an RCRA hazardous or non-hazardous waste. After mixing your holding tank very well, obtain a sample and analyze for pH, Toxicity Characteristic Leach Procedure (TCLP) – Metals (arsenic, barium, cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury, selenium, and silver), copper, tin and zinc. If the pH is between 2 and 12.5 (refer to USEPA regulations 40CFR261.22) and the TCLP metals are below their maximum concentrations (refer to 40CFR261.24), then the waste is likely non-hazardous unless your state EPA also regulates copper, tin or zinc. If this waste is hazardous only because of pH, its pH can be adjusted without a hazardous waste permit under the “elementary neutralization” exemption of 40CFR264.1(g)(6) in order to render it non-hazardous. If it is a hazardous waste due to metals’ concentration(s), it will need to be stored and disposed of as a hazardous waste.
I cannot summarize the requirements for the storage of hazardous waste by generators; you can refer to USEPA regulations under 40CFR262, particularly 40CFR262.34. I believe the initial as well as ongoing costs to comply with these hazardous waste regulations will be less than those for discharge to sewer. If this waste is non-hazardous, the costs will be even significantly less.
RELATED CONTENT
-
Pretreatments: The Next Generation
Emerging technologies can save energy, ease environmental concerns
-
Zinc Phosphate: Questions and Answers
Our experts share specific questions about zinc phosphate and pretreatment
-
Recovery/Recycling Methods for Metal Finishers
A guide to lowering pollution and recovering valuable process constituents.