Capital Cost Estimate Classes
Different levels of capital cost estimates provide key input for decisions over the life of surface finishing projects.
Share
Whether building new process lines or renovating existing lines, capital and operating and maintenance (O&M) cost estimates are important for project planning and implementation. The following is part one in a series that will provide an overview of capital cost estimates classes.
Different levels of capital cost estimates provide key input for decisions over the life of surface finishing projects — from initial concept development through project selection and budgeting and on through completion of engineering design, procurement and implementation phases. Understanding cost estimating methods and expected ranges of accuracy over a typical project life cycle is important for project financial considerations, communications and decision support.
Table 1 is adapted from the AACE International practice guideline 18R-97, which applies the principals of cost estimating classification for process industry engineering, procurement and construction projects. This guideline is applicable for surface finishing process projects. Table 1 shows five AACE cost estimate classifications with the following information and characteristics:
- Comparison of the five AACE classes to the three traditional, widely used ANSI cost estimate classifications.
- Typical uses of each class of estimate for support, from project conceptualization and development through project delivery and completion.
- Level of project definition, expressed as a percentage of engineering and general project (for example, scope, schedule, work breakdown structure, contracting strategy, escalation strategy) documentation development. For process projects, the engineering development typically progresses:
- From early definition, including project location and constraints, general scope, processes and chemistries, production requirements and work envelopes, and process flow diagrams (PFDs).
- Through process layouts and implementation phasing plans (if applicable), piping and instrument diagrams (P&IDs), utility flow diagrams, mass and energy balances, building integration plans, and equipment schedules.
- Through detailed, multidiscipline engineering plans (structural, mechanical, electrical, I&C) and drawings (3D and 2D), specifications and data sheets, functional descriptions, O&M and commissioning plans, and lists of spare parts included in the project.
- Expected Range of Accuracy: The accuracy ranges for each estimate class represent a range around an estimated expected cost value for a specific scope, including appropriate contingencies. The +/- percentage ranges represent an 80% confidence interval that completed actual project costs for a given scope will fall within the estimated ranges (assuming project implementation at specific location, under planned schedule and more). For each estimate class, the ranges for the low expected actual cost and high expected actual cost represent typical variances that result from individual project complexity and level of definition. These ranges also vary with estimating methods, engineering and estimating experience applicable for a specific surface finishing project. The ranges are asymmetric with higher percentage variations for the high costs. This is due to historical cost outcomes for specific project scopes that demonstrate factors combined to make the magnitude of probable final project cost increases from estimated values more likely than cost decreases.
- Other Terms: These other commonly used estimate names are approximately correlated with the AACE estimate classes. Use of these other terms is not always specified with expected ranges of accuracy and may differ in meaning for different circumstances.
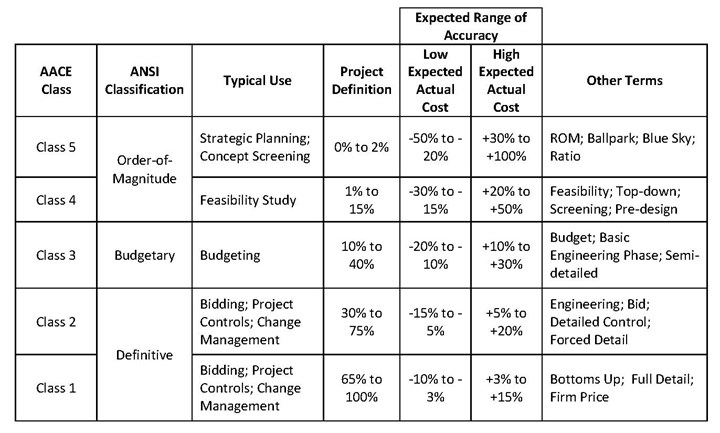
TABLE 1: Summary of AACE International Cost Classifications and Expected Ranges of Accuracy.
In progressing from AACE Class 5 to Class 1 estimates, methodologies typically begin with more stochastic approaches (for example, estimating from previous similar project costs using parametric calculations based on key quantities) and transition to more complete deterministic methodologies (for example, semidetailed to full line item detailed estimates). Appropriate contingencies are assumed to be included in each AACE estimate class. Contingencies are separate from allowances. Contingencies account for nonspecific/uncertain scope items and project risks. Contingencies are best estimated based on experience and review of similar past project estimated scope and costs compared to completed project actual costs with the same scope. When known scope items for a planned project are not included in stochastic extrapolations or are not yet accounted for in line item cost details, specific allowances should be included in estimates for these known but mostly unquantified scope items (for example, existing process demolition that was not part of a previous project used for a Class 5 estimate where the new project has process demolition; interconnecting process electrical or mechanical not yet detailed in a Class 4 or 3 estimate and more).
__________________________________________________
Peter Gallerani is president and chief technology officer at Integrated Technologies, Inc., an engineering, design and consulting solutions firm based in Burlington, Vermont, that offers project planning and development, full-service engineering and design, project and construction management, and services during construction to the surfacing finishing and industrial manufacturing industries. Visit processengineer.com
Related Content
3 Tests to Ensure Parts are Clean Prior to Plating
Making sure that all of the pre-processing fluids are removed prior to plating is not as simple as it seems. Rich Held of Haviland Products outlines three tests that can help verify that your parts are clean.
Read MoreThe Future of Hard Chrome: Pioneering Innovations for Sustainable Solutions
Although useful, chromic acid and other compounds that contain hexavalent chromium ions are highly toxic and carcinogenic. However, one company has developed an alternative for the hard chrome process that achieves thick, conformal coatings with wear and fatigue resistance comparable or superior to hexavalent chromium-based systems.
Read More5 Common Electroplating Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Electroplating requires adherence to process control and maintenance procedures — here are some common missteps to avoid.
Read MoreSwitching from Hexavalent to Trivalent Chromium Plating
There are advantages and disadvantages of moving from hexavalent to trivalent baths. When considering this choice, gather the facts from this article in order to make a well-educated decision.
Read MoreRead Next
The Best Tape for High-Temperature Applications
High-temperature tapes are designed with maximum heat ratings indicating the highest temperature they can withstand for a very short time.
Read MoreReducing Material Use and Overspray
Looking for applicators or process improvements for reducing material use and overspray? Binks offers helpful advice for searching out new solutions.
Read More



















