10 Anodizing Best Practices
Following this list of guidelines can help to increase the performance, cost effectiveness and quality for your anodizing operation.
#asktheexpert
Edited by Scott Francis

Anodizing is one of the most common surface treatments of aluminum. In all anodizing processes, the basic reaction is conversion of the aluminum surface to aluminum oxide. The aluminum part, when made anodic in an electrolytic cell, causes the oxide layer to become thicker, leading to better corrosion and wear resistance. For decorative purposes, the oxide layer formed on the surface can be dyed. In aluminum anodizing processes, the basic reaction is a conversion of the aluminum surface to aluminum oxide, including Type I (Chromic acid anodizing), Type II (Sulfuric acid anodizing), Type III (Hard coat anodizing).
Below are ten best practices to keep in mind when anodizing:
- Surface Preparation: Thorough cleaning of the metal surface before anodizing to remove any contaminants, oils or oxides is imperative. Common methods include alkaline cleaning and acid etching.
-
- Learn more: The pretreatment processes prior to anodizing are critical in not only cleaning the aluminum, but also in creating a variety of colors and finishes. Learn more about the effect of pretreatment on the appearance of anodic coating. short.pfonline.com/anodizepretreat
-
- Alloy Considerations: Different aluminum alloys respond differently to anodizing. It is important to keep this in mind when setting finish and performance expectations.
-
- Learn more: Alloys with higher silicon concentrations can inhibit the growth of anodic oxide films under galvanostatic and potentiostatic conditions. short.pfonline.com/intermetallicspec
-
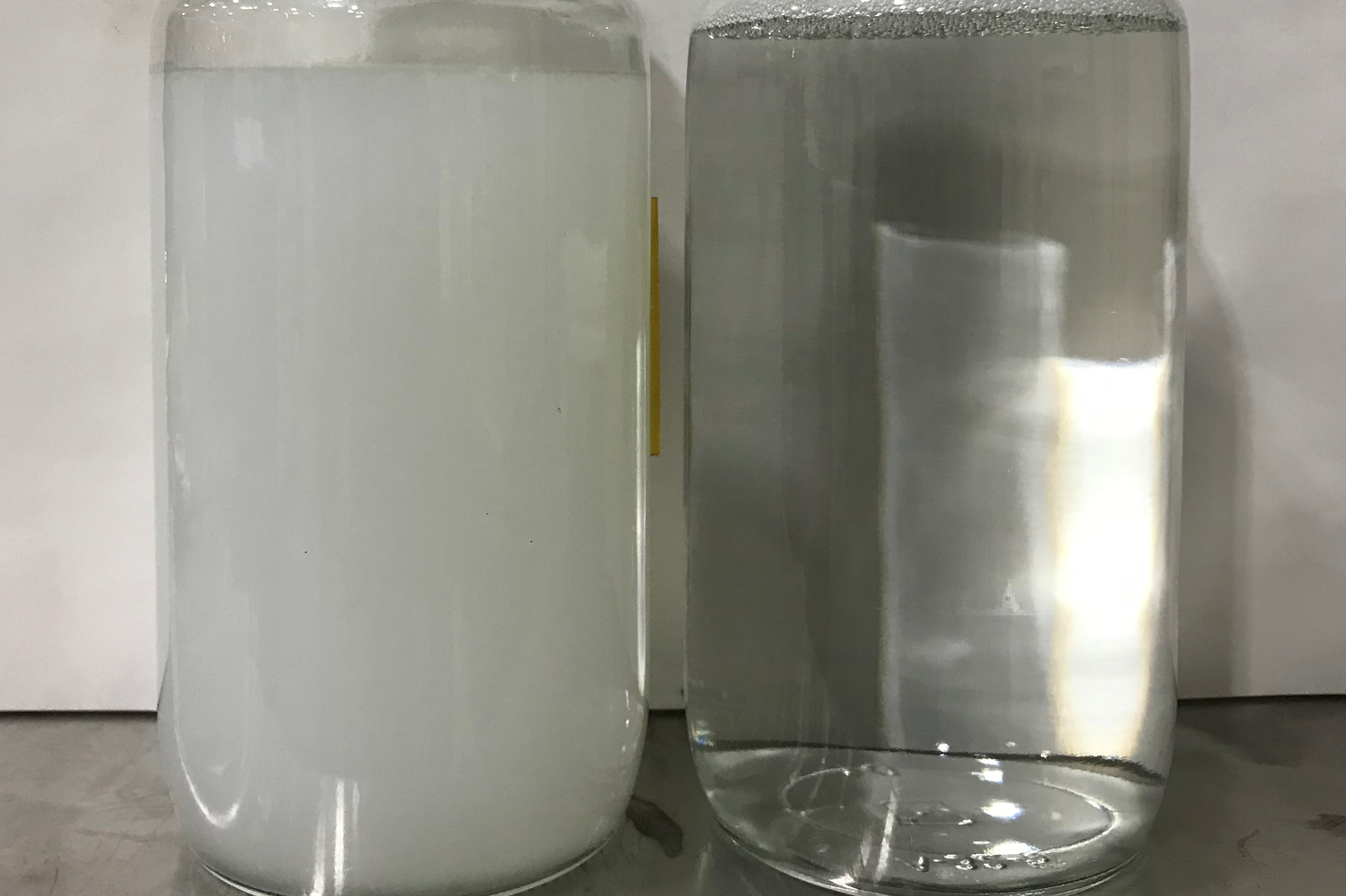
- Quality Control: Consistent monitoring of your anodizing process through regular titrations will help maintain the desired coating thickness, color consistency and surface finish.
-
- Learn more: Having trouble with spotting defects when anodizing? This overview of the various causes of white spots and potential solutions may help. short.pfonline.com/anodizewhitespots
- Learn more: Understanding the differences in cracking and crazing in anodic coatings, and insights for mitigating defects in anodized parts: short.pfonline.com/crackcraz
-
-
-
- Learn more: Sulfuric acid anodizing bath makeup. short.pfonline.com/sulfanodiz
- Learn more: The 720 Rule describes the relationship between the amount of current passed through an aluminum surface and the resultant anodic oxide thickness produced over time. short.pfonline.com/720rule
-
-
-
- Learn more: Aluminum sulfate is the preferred buffer to prevent burning of parts in an anodizing bath. short.pfonline.com/sulfbuff
-
- Sealing: Proper sealing helps in closing the pores of the anodized layer and enhances the corrosion resistance and durability of the coating.
-
- Learn more: Is a cold seal right for your anodizing operation? short.pfonline.com/coldseal
- Learn more: Sealing of anodized aluminum is considered to be the most important of all the various steps in the anodizing process. Learn how to select the best anodizing seal process: short.pfonline.com/selectseal
-
- Dyeing: Take care to adhere to proper dyeing techniques to achieve uniform and vibrant colors and make sure the dye is compatible with the anodized coating for long-lasting results.
-
- Learn more: How to minimize fading of anodized colors. short.pfonline.com/anofade
-
- Racking Considerations: Properly designed and maintained racking aids in achieving uniform coating thickness and prevents uneven coloration.
-
- Learn more: What are the most common racking problems for platers and anodizers? This helpful clinic will help you avoid the common pitfalls: short.pfonline.com/rackingpitfalls
-
- Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation in the anodizing facility to control fumes and maintain a safe working environment. Proper ventilation also aids in controlling temperature and chemical concentrations.
-
- Learn more: Read about pollution control for anodizing: short.pfonline.com/pollano
-
-
-
- Learn more: Considerations for the ventilation of metal finishing tanks. short.pfonline.com/opentank
-
- Preventative Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain anodizing equipment, including rectifiers, tanks and filtration systems. Well-maintained equipment contributes to consistent anodizing results.
-
- Learn more: Tips for optimizing your anodizing line: short.pfonline.com/anomaint
-
- Waste Management: Implementation of effective waste management practices and compliance with environmental regulations is critical for conserving resources, controlling costs and minimizing the environmental impact of the anodizing process.
-
- Learn more: Read about one anodizer’s success in conserving water and reducing waste after implementing a zero liquid discharge facility: short.pfonline.com/0discharge
-
These are just a few tips to help ensure a successful anodizing process with consistent and high-quality results. Always consult with anodizing experts and follow industry standards in order to keep up with the latest advancements in anodizing technology.
Scott Francis
Scott Francis is the editor-in-chief of CompositesWorld and Products Finishing media brands, properties of Gardner Business Media. He has also edited for the Writer's Digest, HOW, Popular Woodworking media brands and has authored books on a range of topics. Scott has a bachelor’s degree in writing and editing and a minor in biology from Western Carolina University. PRESS KIT
RELATED CONTENT
-
Cleaning, Pretreatment to Meet Medical Specs ISO 13485 or FDA 21 CFR820
Maximilian Kessler from SurTec explains new practices for industrial parts cleaning, metal pretreatment and decorative electroplating in the medical device industry.
-
What Causes Discoloration of Clear Coat Powder?
Coaters sometimes have problems with cloudy appearance or yellowing of the coating, and expert Rodger Talbert has a few possible solutions.
-
Preventing Anodizing Cathodes from Turning Red
While the red color may not be desirable, anodizing expert Drew Nosti says it poses no particular problem to a successful anodizing process.