Graphite Cleaning
Question: Our company produces aluminum extrusions for paint.
Question:
Our company produces aluminum extrusions for paint. During the extrusion process, the aluminum is carried over graphite blocks, with graphite contamination adhering to the aluminum surface.
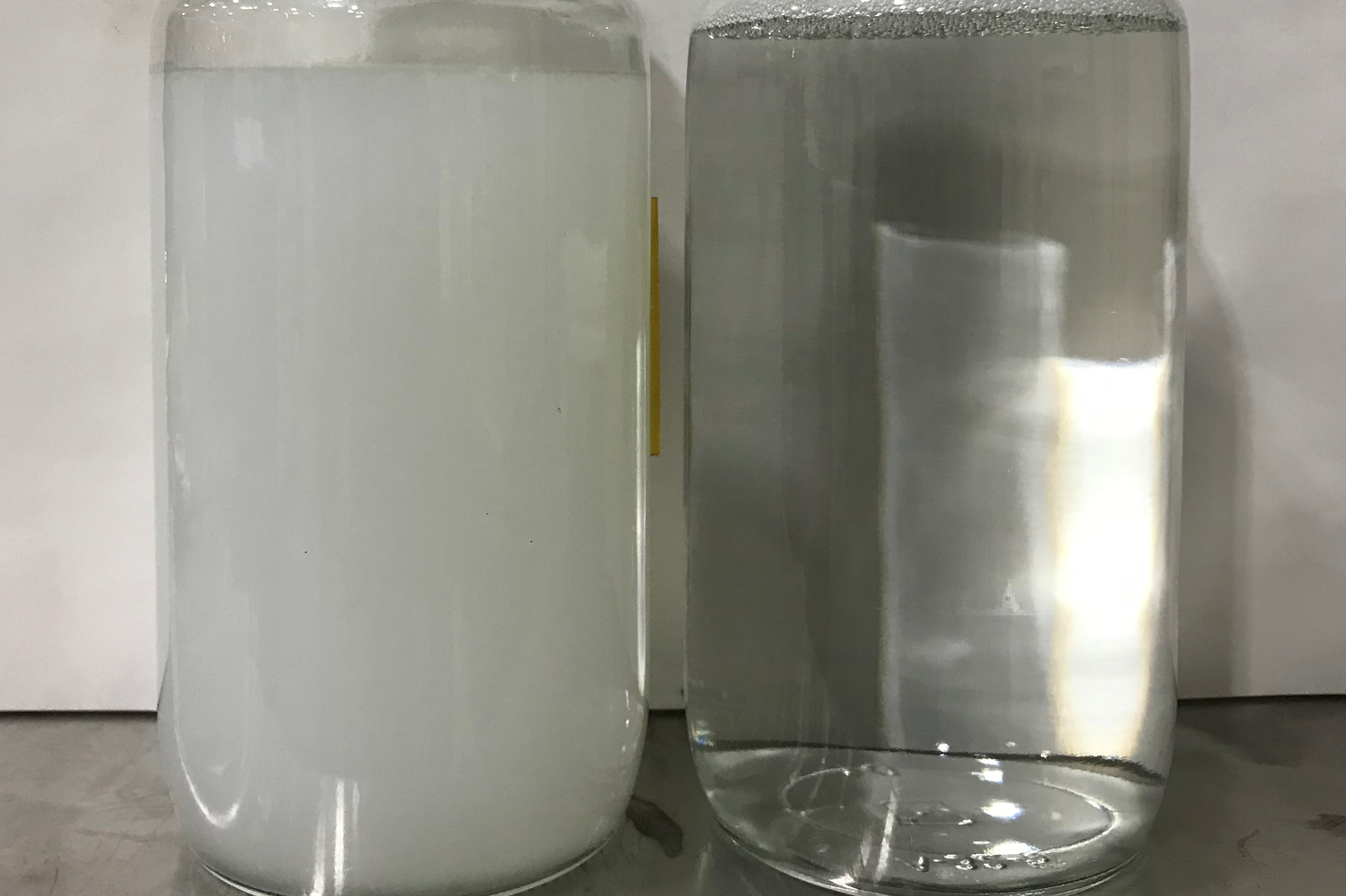
We use an immersion bath to clean, rinse and chrome pretreat. Our current cleaning tank is made with an alkaline cleaner, but it does not remove the graphite, causing many lost hours due to hand wiping. We have attempted to use a 60 g/liter caustic bath, but this causes such a reaction that the metal begins to float, etching begins between the spacers separating the metal (causing high spots and sanding), and the caustic is difficult to rinse off as it cools during transfer to the rinse tank. We have separately racked each individual piece, however, load size is very small, again affecting productivity. A number of suppliers have indicated they have products that will meet our required specification, but with no luck for many years. Any suggestions? T.P.
Featured Content
Answer:
The two products you describe appear to be on opposite ends of the spectrum. The first cleaner you mentioned is alkaline and presumably did not etch the extrusions at all, so it must be inhibited. An inhibited cleaner contains sodium metasilicate to eliminate base metal attack on the aluminum. While the cleaner may be fairly effective for removing grease and oils, it may be no more effective than a neutral cleaner on the graphite, which is a physical particulate contaminant as opposed to a film of oil that is emulsified or saponified for removal. The physical nature of the graphite contamination would likely necessitate some sort of mechanical action to facilitate the removal of it. This could be accomplished in a few ways.
One way (probably the easiest to implement) would be to modify the existing caustic etch you are performing. The bubbles created at the metal surface are effective in undercutting and lifting soils from the surface of the part. Ideally, the parts should be degreased prior to etching, otherwise you risk uneven metal removal.
From what you describe, it does not sound like you need to perform the etching as vigorously as you indicated you are doing it. The metal removal rate indicated by the difference between low and high spots that you are sanding indicate too much time, temperature or concentration (or a combination of all three). A room temperature caustic bath at the concentration you described should lift the graphite contamination in relatively short time, long before you etch away the amount of base metal described. I would think that in as little as 30 sec you may be able to etch away enough base metal to remove the graphite. From what you describe, I am estimating that you're spending as much as 10 min in the caustic etch bath. Additionally, you always need to follow a caustic etch of aluminum with a desmut. This is often done with a room temperature nitric acid solution (around 25% by volume). If there is residual caustic that is not removed in the rinse tank, the nitric acid will help take it off.
The mechanical agitation from spray washing with a moderately alkaline cleaner that would provide some etch to the surface may also be quite effective. The etch rate and total exposure time would be less, but the impingement force from the spray washer may be sufficient to lift and remove much of the graphite contamination.
I am not sure about the feasibility of the final suggestion, but if the geometry of the extrusion is amenable to this, an automated wipe may be fairly effective at the removal of the graphite, along with the action of a cleaning solution.
RELATED CONTENT
-
The Hull Cell: Key to Better Electroplating - Part II
How to use it for planning, preventive maintenance and troubleshooting.
-
Are TGIC-Free Powder Coatings Right For You?
This alternative to TGIC-based polyester powder coatings offers similar performance and enhanced transfer efficiencies.
-
Zinc Phosphate: Questions and Answers
Our experts share specific questions about zinc phosphate and pretreatment