Hexavalent to trivalent chromium — the environmental benefits
Regulatory pressures to switch from hexavalent chromium to trivalent alternatives are a growing concern for many finishing operations. In this Products Finishing Ask the Expert clinic, Brittany McKinney of Pavco discusses the environmental considerations driving these regulations.
#asktheexpert #regulation #sustainability

Q: What are some environmental benefits of switching from hexavalent chrome to trivalent chrome?
A: Chrome plating is a surface finishing process that involves electroplating a thin layer of chromium onto a metal object. This process enhances the object’s appearance, improves its corrosion resistance, and provides desirable properties. Chrome plating is widely used in various industrial applications due to its decorative and functional benefits. The use of chrome plating varies from decorative applications, aerospace industries, machinery and equipment, medical equipment, and many other industrial applications. Hexavalent chrome plating is widely used, but many environmental concerns should make companies consider switching to trivalent chrome plating.
Featured Content
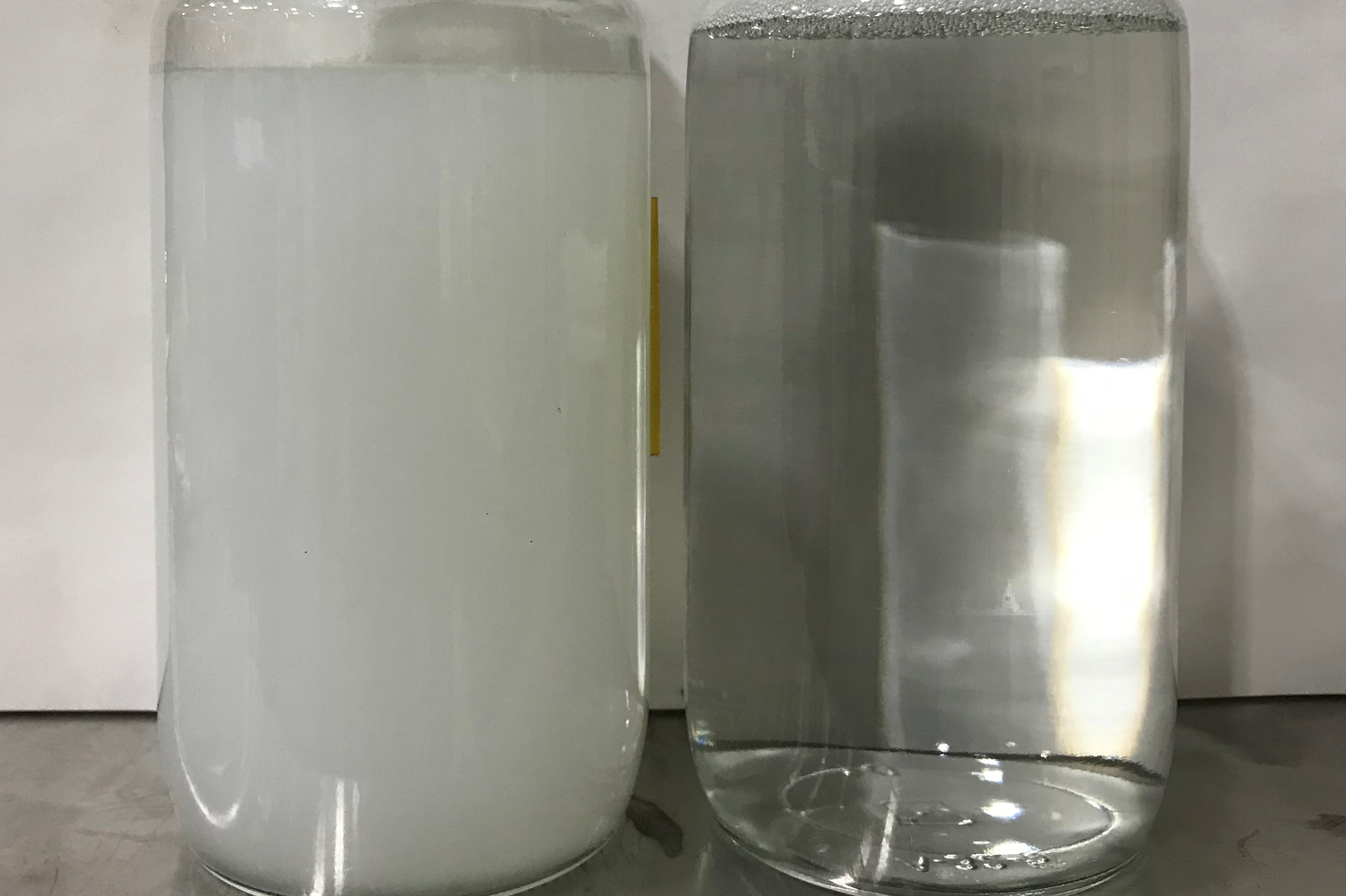
Hexavalent chrome compounds are known to be highly toxic and carcinogenic. Prolonged exposure to hexavalent chromium can lead to serious health issues, including lung cancer, respiratory irritation, and skin conditions. Trivalent chrome is believed to be less readily absorbed by the human body compared to hexavalent chrome. This means that the potential for adverse health effects is reduced when switching to trivalent chrome plating. Hexavalent chrome is also more soluble in water, which can lead to increased environmental contamination if not properly managed. The waste treatment process for hexavalent chrome is not only more costly but also time consuming, and if not done accurately, it could contaminate the environment. Switching to trivalent chrome plating will generate less hazardous waste, lower disposal costs, and reduce environmental impacts from the handling and disposal of hazardous waste.
Hexavalent chrome plating solutions typically have issues with misting. To minimize and eliminate the misting of the solution, a mist suppressant is used, which contains PFAS/PFOS. Polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and Perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) are a group of human-made chemicals that have been used in a variety of industrial and consumer products for decades. PFAS/PFOS are persistent in the environment, meaning they do not easily break down over time. The forever chemicals have been associated with various health risks, including developmental effects, liver damage, immune system dysfunction, and an increased risk of certain cancers. Exposure to PFAS/PFOS in regard to hexavalent chrome plating can occur through contaminated air, water and soil. Bioaccumulation also occurs which means the concentration continues to increase over time in the blood and organs of those that come in contact with the chemicals.
Not only is the toxicity and waste treatment more environmentally harmful with hexavalent chromium, it also has significantly higher energy requirements compared to trivalent chromium. Trivalent chrome plating solutions are typically operated at much lower temperatures. The efficiency in terms of metal deposition is also much higher with trivalent chrome plating. This efficiency can lead to a reduction in the duration of the electroplating process, thereby lowering the overall energy consumption required for the complete plating process of any given object. The deposition rate and coating thickness is much easier to control with trivalent chrome, allowing for more efficient use of energy during the plating process. The reduced temperature requirements and improved efficiency associated with trivalent chrome plating allows for smaller equipment and more compact plating setups which leads to less energy use for operation. Trivalent chrome plating does not require extensive ventilation systems to control emissions and protect workers, in comparison to hexavalent chrome.
Researchers are continuously developing and optimizing trivalent chrome plating formulations to enhance efficiency and performance. This includes improving the bath stability, deposition rate, and adhesion properties while minimizing the environmental impact. Ongoing studies are researching ways to optimize the trivalent chrome plating process to reduce energy consumption. Some of these studies include exploring the use of advanced control systems, automation, and innovative electrode designs to improve the efficiency of metal deposition. The goal of ongoing research and development in the chrome plating industry is to strike a balance between maintaining the functionality and performance of chrome-plated products while minimizing the environmental impact associated with the plating processes. Continuous innovation and the adoption of sustainable practices will contribute to the overall improvement of environmental performance in the chrome plating industry.
About the Author

Brittany McKinney
Brittany McKinney is a Technical Service Engineer at Pavco Inc. Visit pavco.com.
RELATED CONTENT
-
Top Reasons to Switch to a Better Cleaning Fluid
Venesia Hurtubise from MicroCare says switching to the new modern cleaning fluids will have a positive impact on your cleaning process.
-
Improving Transfer Efficiencies in Coating Operations
There are many methods for addressing electrostatic grounding in metal painting processes, and Tim Ulshafer from Mueller Electric says the best method for your process is a simple and worthwhile exercise.
-
Understanding Paint Atomization
BASF coatings development expert Tim December explains how paint atomization works for both pneumatic spray applicators and high-speed rotary bell applicators.