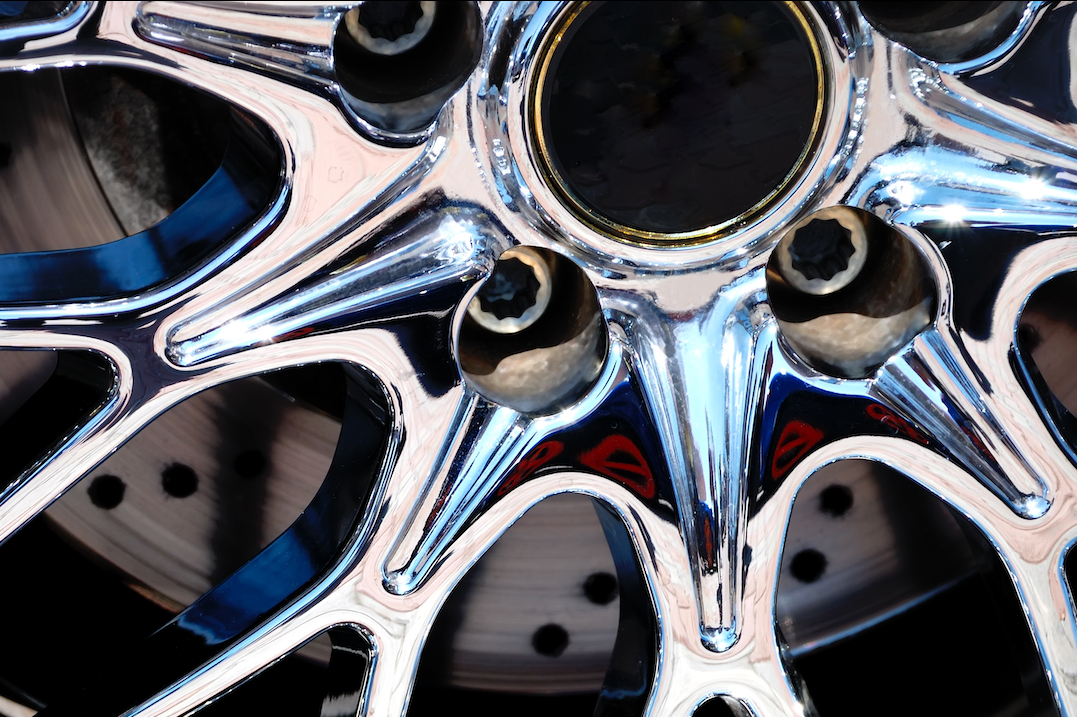
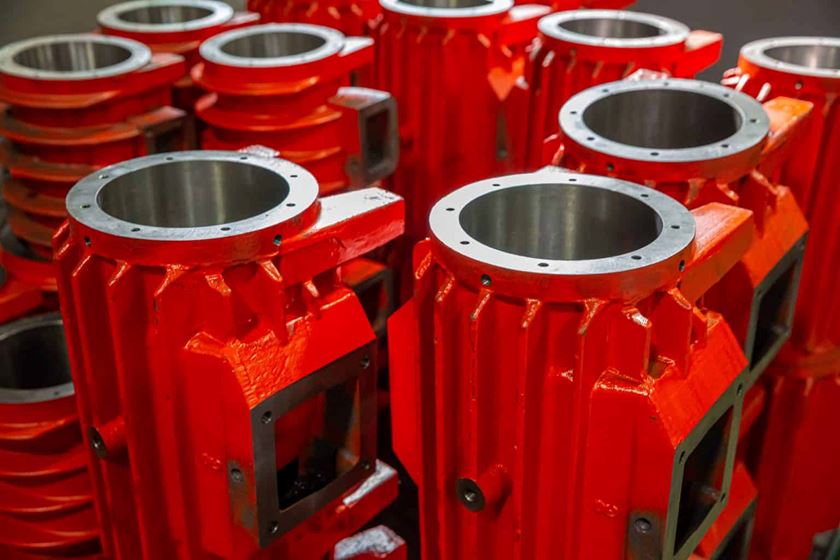
Monorail Shot Blaster
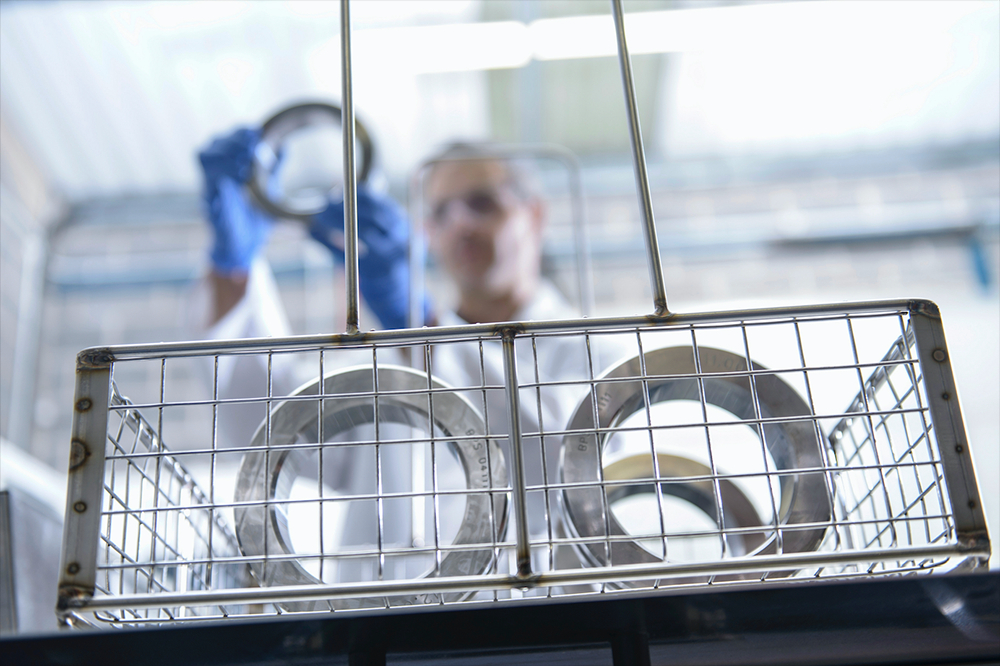
LS Industries' monorail blaster on display at SUR/FIN 2021
#surfin
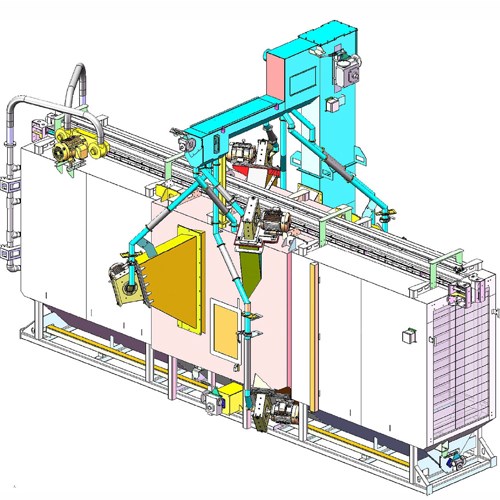
LS Industries’ monorail blasters are versatile machines for handling blasted materials. Monorail blasters are designed to be able to blast all sides of the material in the blast zone.
Whether you are adding a new product handling monorail to your facility or you already have something in place, LS Industries can design a monorail blaster to work for your needs.
LS Industries | 316-265-7997 | lsindustries.com
RELATED CONTENT
-
Defects in Hard Chromium Deposits Part I: Causes and Cures
The causes of and remedies for defects in hard chromium deposits are explored in the first of this two-part P&SF article from 1984. Photomicrographs and SEM (scanning electron microscope) photographs will illustrate that most defects in various hard chromium deposits arise from defects in the basis metal. These defects may be in the original metal surface or may be caused by preplate finishing. Homogeneous hard chromium deposits can be produced only by eliminating these defects. Practical suggestions and procedures will be given.
-
Electroless Nickel Coatings: Appearance, Gloss and Surface Morphology
For decorative coatings, appearance is the essential purpose for application, but also for functional surface finishes it becomes increasingly relevant as an added value on top of specified technical requirements. Appearance is affected by spectrum and intensity of incident light, roughness and morphology of the coating surface, optical properties of the coating material, eventual superficial oxide films, and individual perception. The predominant factor is surface roughness, which in turn depends on base material roughness, quality of substrate pretreatment, and nucleation and growth kinetics of the electroless nickel (EN) deposit. Interdependency of gloss measurements with roughness measurements and with chemical composition of coatings was investigated for new generation mid-P EN processes and compared to traditional ones.
-
A Pulse/Pulse Reverse Electrolytic Approach to Electropolishing and Through-Mask Electroetching
Research at the authors’ laboratories has focused on pulse/pulse reverse electrolysis on cathodic processes, such as hard chromium plating from non-hexavalent chemistries. This papers describes studies into pulse/pulse reverse electrolysis as applied to electrochemical metal removal processes, such as electropolishing and electroetching.