Anodizing is one of the most common surface treatments of aluminum. In all anodizing processes, the basic reaction is conversion of the aluminum surface to aluminum oxide. The aluminum part, when made anodic in an electrolytic cell, causes the oxide layer to become thicker, leading to better corrosion and wear resistance. For decorative purposes, the oxide layer formed on the surface can be dyed.
In aluminum anodizing processes, the basic reaction is a conversion of the aluminum surface to aluminum oxide, including Type I—Chromic acid anodizing, Type II—Sulfuric acid anodizing, Type III—Hard coat anodizing.
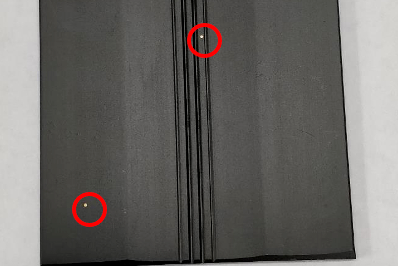
Understanding and Managing White Spots on Anodized Aluminum
Having trouble with spotting defects when anodizing? Taj Patel of Techevon LLC offers a helpful overview of the various causes of white spots and potential solutions.
Anodizing: Essential Reading
Anodizing for Bonding Applications in Aerospace
Anodizing for pre-prep bonding bridges the gap between metallic and composite worlds, as it provides a superior surface in many applications on aluminum components for bonding to these composites.
Zinc Electroplating
Choosing the best process for your operation.
Preventing Anodizing Cathodes from Turning Red
While the red color may not be desirable, anodizing expert Drew Nosti says it poses no particular problem to a successful anodizing process.
Deoxidizing Aluminum as a Pretreatment
This important first step can help prepare the metal for subsequent surface finishing.
Cleaning, Pretreatment to Meet Medical Specs ISO 13485 or FDA 21 CFR820
Maximilian Kessler from SurTec explains new practices for industrial parts cleaning, metal pretreatment and decorative electroplating in the medical device industry.

FAQ: Anodizing
What is anodizing?
Anodizing refers to a broad range of surface treatments commonly applied to various grades of aluminum and titanium to provide cosmetic and functional benefits.
https://www.pfonline.com/articles/understanding-the-hidden-costs-and-benefits-of-anodizing
What is a cold seal?
A cold seal, also known as a room-temperature seal, is a sealing bath that contains nickel and fluoride and is used at ambient temperatures. Best results are obtained with temperature regulation, which ensures a more consistent rate of sealing reaction. Recommended sealing temperatures for Clariant cold seal products are between 80° and 90°F (27° to 32°C).
https://www.pfonline.com/articles/is-a-cold-seal-right-for-your-anodizing-operation
What is the best anodizing seal process for my operation?
Sealing of anodized aluminum is considered the most important of the various steps in the anodizing process. How you seal determines the performance of the anodic oxide in its end-use environment. After the anodic oxide layer is formed, there are a number of sealing options that exist, including unsealing, high temperature, mid-temperature, and room-temperature or cold sealing.
https://www.pfonline.com/articles/selecting-the-best-anodizing-seal-process-
How do I evaluate anodized aluminum?
- Film thickness measurement
- Curvature
- Edge Effect
- Base metal thickness
- Surface roughness
- Conductivity
- Quality of Seal
https://www.pfonline.com/articles/test-methods-for-evaluating-anodized-aluminum